Introduction: Although outcomes for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) have improved with recent advances in treatment, relapse is still frequent. Early relapse is associated with poorer outcomes (Majithia et al., Leukemia 2016;30:2208-13) and is thought to reflect more aggressive disease, particularly within 12 months of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). In the randomized phase 3 CANDOR study, progression-free survival (PFS) was significantly improved in patients with relapsed or refractory MM (RRMM) receiving carfilzomib, dexamethasone, and daratumumab (KdD) compared with carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd) (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03158688; Usmani et al., Blood 2019;134:LBA-6). In this post hoc analysis of the CANDOR study, we studied the safety and efficacy of KdD vs Kd in patients with early or late relapse following the most recent therapy.
Methods: In the CANDOR study, patients with RRMM who received 1-3 prior lines of therapy were randomized 2:1 to receive KdD or Kd. The primary endpoint was PFS; secondary endpoints included overall response rate (ORR), rate of complete response or better (≥CR), and safety. In this analysis, subgroups were defined by relapse timing following the most recent therapy. Relapse <12 months from initiation of the most recent line of therapy was defined as early, and relapse ≥12 months from initiation of the most recent line of therapy was defined as late (except for the subgroup of patients who received only one prior line of therapy, where a cutoff of 18 months was used to define early and late relapse). For the subgroup of patients with prior ASCT, relapse <12 months following prior transplant was classified as early, and relapse ≥12 months following prior transplant was classified as late. Median PFS was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, while hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs were estimated from a nonstratified Cox regression model. Response rates were defined per the International Myeloma Working Group Uniform Response Criteria.
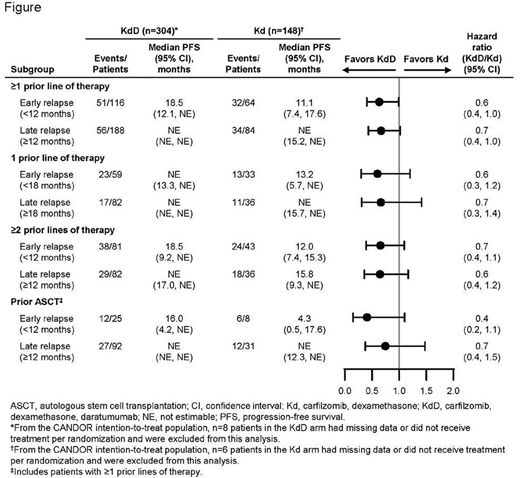
Results: In total, 452 patients (156 of whom received prior ASCT) were included in this post hoc analysis; 210 patients received 1 prior line of therapy, and 242 patients received ≥2 prior lines of therapy. PFS HRs (KdD vs Kd) were consistent across subgroups regardless of early or late relapse, including in patients with prior ASCT (Figure). In patients who received 1 prior line of therapy, the ORR was 86.4% vs 57.6% for early relapsers in the KdD vs Kd arms and 93.9% vs 88.9% for late relapsers, respectively. The rate of ≥CR was 28.8% vs 3.0% for early relapsers and 39.0% vs 16.7% for late relapsers. In patients who received ≥2 prior lines of therapy, the ORR was 75.3% vs 65.1% for early relapsers in the KdD vs Kd arms and 82.9% vs 86.1% for late relapsers. The rate of ≥CR was 19.8% vs 4.7% for early relapsers and 28.0% vs 16.7% for late relapsers. The rates of grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) observed in the early and late relapse subgroups were similar to that in the overall CANDOR population.
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis from the phase 3 CANDOR study, efficacy results were generally consistent across early and late relapse subgroups. In particular, rates of ≥CR were higher with KdD vs Kd among patients with early relapse. The rates of grade ≥3 TEAEs were consistent with the safety profile of overall KdD and Kd cohorts. These results support the use of KdD in patients with RRMM, regardless of early or late relapse, prior ASCT, or whether patients relapsed after one prior line of therapy or 2 or more prior lines of therapy.
Weisel:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Adaptive: Consultancy, Honoraria; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Geils:Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Karlin:Celgene: Other: Personal fees; Sanofi: Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support, personal fees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support, personal fees; Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support, personal fees. Mollee:Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Caelum: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS/Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sunami:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Alexion Pharma: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ono: Honoraria, Research Funding. Goldrick:Amgen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Fang:Amgen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Fowler:Amgen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Mateos:EDOMundipharma: Consultancy; Adaptive: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmamar: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncopeptides: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Carfilzomib is a proteasome inhibitor and daratumumab is an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, which can both be used to treat RRMM.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal